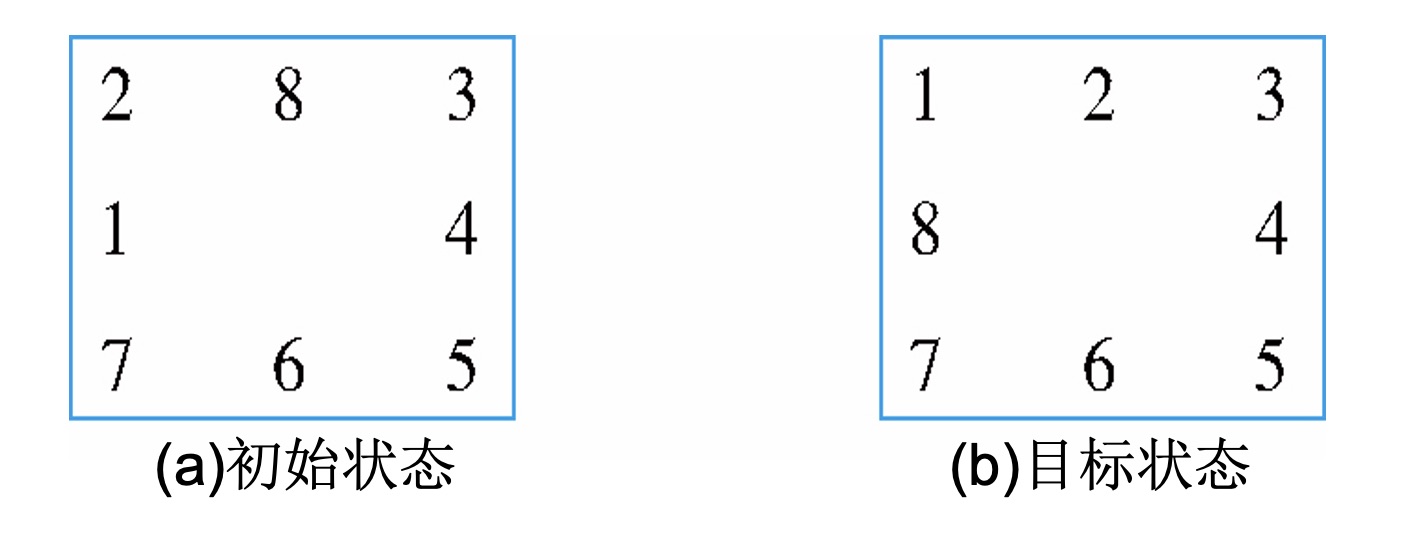一、实验要求
这次实验要求我们用A算法求解八数码问题。
八数码问题是指,在一个3*3的棋盘上,存在8个棋子和1个空位,其中每个棋子都可以向上下左右四个方向移动(若存在空位)。给定一个初始状态和目标状态,要求找到从初始状态变换至目标状态的最短路径,输出步数和路径中的状态。
 8-puzzle
8-puzzle
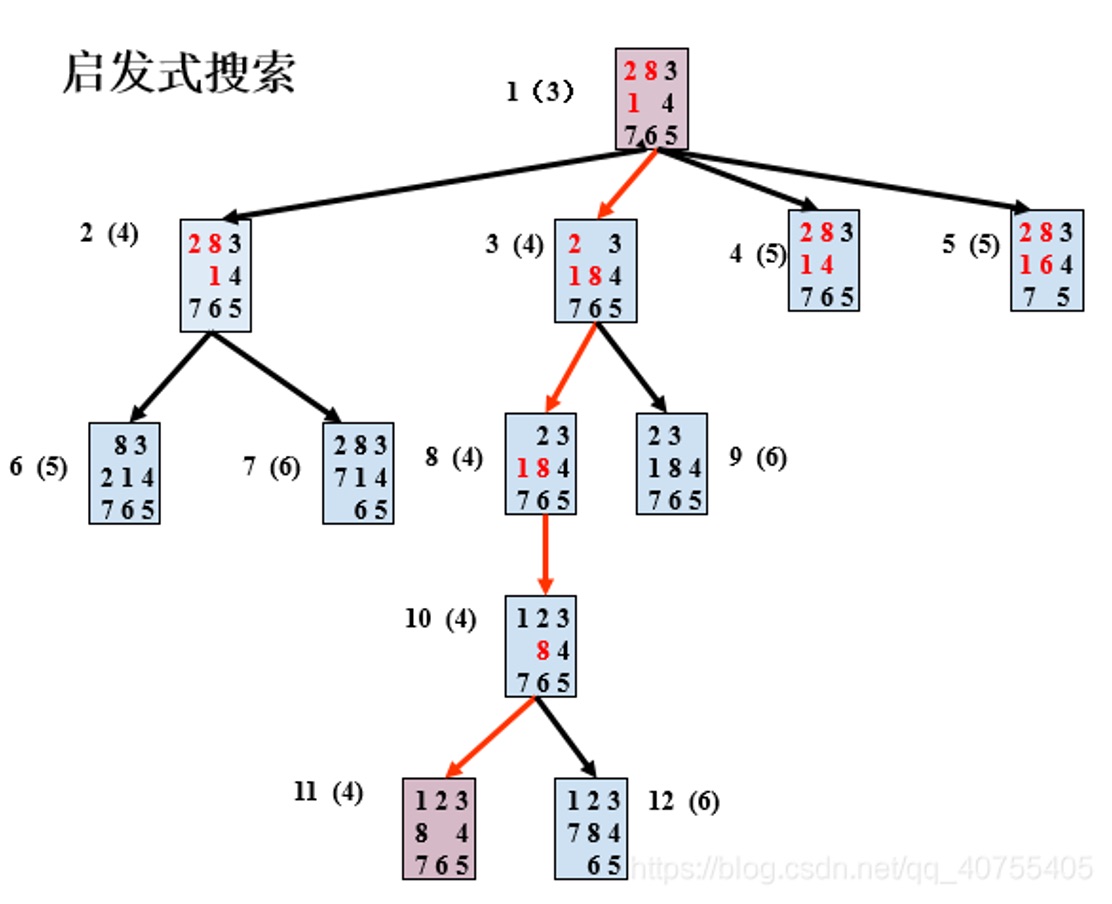
而启发式搜索算法则是一种状态空间树搜索算法。我们首先根据问题定义一个启发函数h,将h的值作为当前状态与目标状态之间的“差距”,用以判断当前状态的“好坏”。随后,我们对所有未扩展状态进行按估值h进行排序,每次都扩展当前最“好”的状态,直至找到目标状态,或是完全遍历状态空间树(无解)。
 heuristic-algorithm
heuristic-algorithm
二、算法设计
A算法最核心的地方就在于针对具体问题设计良好的启发函数h,剩下只需要用一个优先级队列存储所有未扩展状态,按h大小排序,挨个扩展并计算搜索深度(即步数)即可。因为这次实验要求我们给出结果路径的中间状态,所以还需要把已扩展节点也进行储存,并且在扩展过程中保留好路径信息。
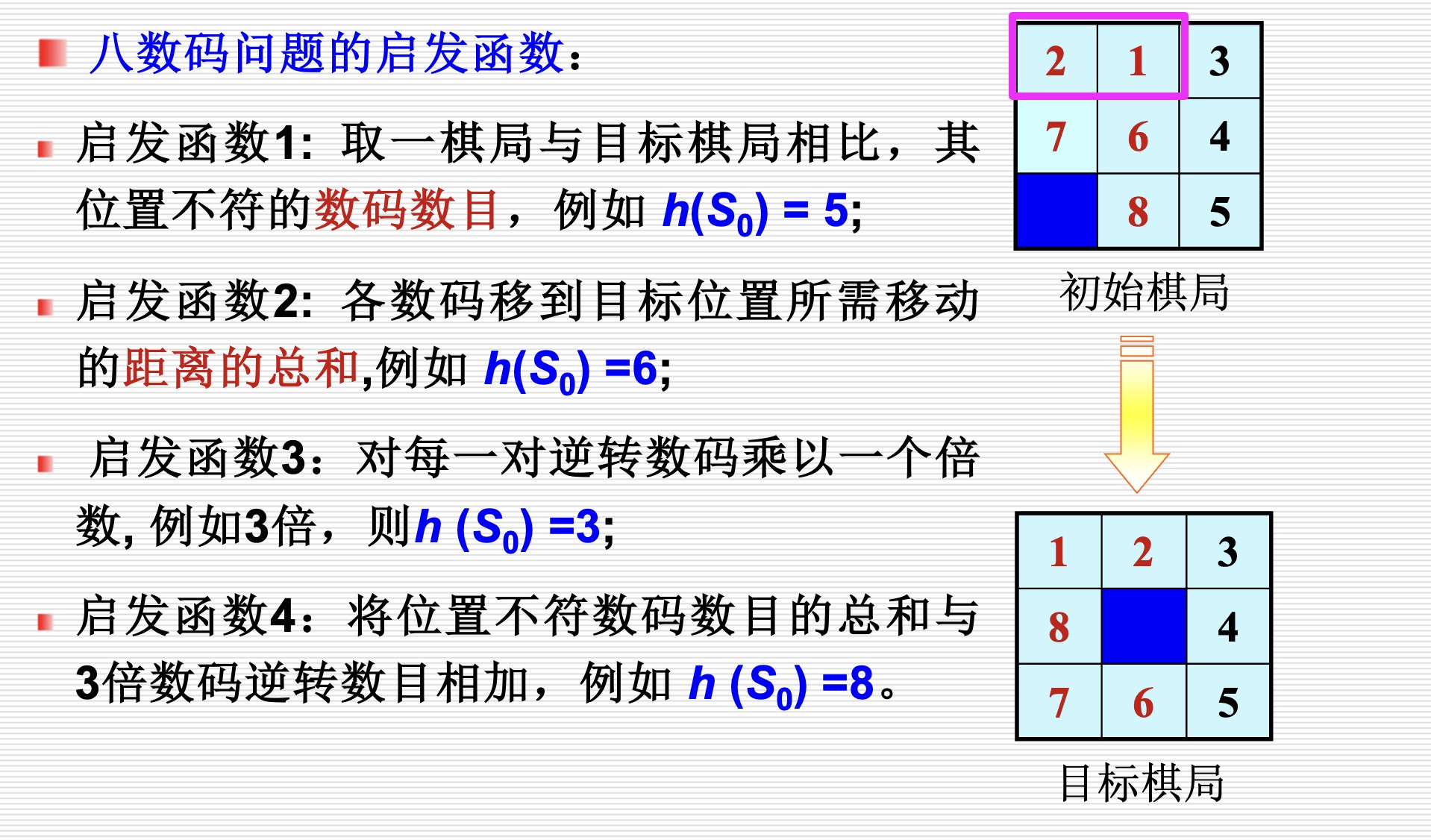
估值函数上,这次实验给了四种h函数的备选,我们从中选择一个进行实现即可。
 heuristic-function
heuristic-function
我选了曼哈顿距离和(启发函数二)作为启发函数,曼哈顿距离是指两个点坐标之间的绝对轴距之和,是一种很简单但很经典的启发函数。我们只需计算当前状态中每个点与目标状态中对应点的曼哈顿距离之和,便可以得到当前状态的估值h,h值越小代表状态与目标状态越接近,也就是状态越“好”。
 Manhattan-distance
Manhattan-distance
算法设计完成,下面就可以Coding了(这次还是用了C++)。
Define
首先是一些定义和初始化工作。定义状态结构体Node,存储对应的棋盘状态,估值h,步数depth。同时,因为对输出路径的要求,还需要存储状态id,以及其父状态parent,用于回溯求解路径。随后,我们需要定义用于优先级队列排序的比较函数,定义曼哈顿距离h更小的状态更优,而在h相等的情况下,我们应优先选择步数更少的状态。同时,我们定义存储未扩展节点的优先级队列open,用于回溯路径的已扩展节点序列close和路径path。最后,我们还需定义目标状态中各点的坐标。
DEFINE1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| struct Node {
int map[3][3];
int h, depth;
int id, parent;
};
struct cmp {
bool operator()(Node a, Node b) {
if(a.h > b.h)
return 1;
else if(a.h < b.h)
return 0;
else
return a.depth > b.depth;
}
};
priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, cmp> open;
vector<Node> close;
vector<Node> path;
int end_loc[8][2] = {{0, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, 2}, {1, 2}, {2, 2}, {2, 1}, {2, 0}, {1, 0}};
|
Manhattan Distance
下面根据曼哈顿距离算法编写启发函数h。计算map中除0(即空位)外所有点与目标状态下的曼哈顿距离,并不断加和即可。
ManhDis1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
int H(int map[3][3]) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
int num = map[i][j];
if (num == 0) continue;
sum += abs(i - end_loc[num - 1][0]) + abs(j - end_loc[num - 1][1]);
}
}
return sum;
}
|
Other Functions
随后再定义一些辅助函数。例如checkSame函数,用于检验当前状态是否在open或close序列中存在,以避免对状态的重复搜索。以及print_info函数(可选),用于在搜索过程中输出每次扩展的状态信息,辅助调试。
HELPER1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
bool checkSame(Node t) {
for (int i = 0; i < close.size(); i++) {
bool same = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
if (close[i].map[j][k] != t.map[j][k]) {
same = 0;
break;
}
}
}
if (same)
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void print_info(Node cur) {
cout<<"当前状态:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
cout<<cur.map[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<"id: "<<cur.id<<endl;
cout<<"parent: "<<cur.parent<<endl;
cout<<"depth: "<<cur.depth<<endl;
cout<<"曼哈顿距离:"<<cur.h <<endl;
cout<<endl;
}
|
Init
下面进入main函数。首先是初始化部分,要求用户输入初始状态(以数字0表示空位),设置其相关信息,并将初始状态加入未扩展节点列表。
INIT1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| Node start;
cout<<"请输入初始状态:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
cin>>start.map[i][j];
}
}
start.h = H(start.map);
start.depth = 0;
start.id = 0;
start.parent = -1;
open.push(start);
|
Search
随后,开始对状态空间树的搜索。我们从open队列中取出最优的状态,检查其是否为目标状态(后续给出)后,尝试对其进行变换,搜索其子状态。对于状态的变换,虽然实际的定义是尝试让每个棋子向上下左右四个方向移动,但由于只有移动至空格位置才能变换成功,因此可以等效为尝试将空格进行上下左右四个方向(处于边界则移动失败)的移动。因此,我们可以分别尝试四种移动。对于每次变换后的子状态,我们首先更新其棋盘,并根据棋盘进行相同状态检索。若该状态已经检索过,则跳过。否则,我们应计算其估值,步数,id等信息,并记录其父状态的id,以便后续回溯求解路径。最后,我们将该状态加入未扩展状态队列open中,并继续搜索下一子状态。
SEARCH1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
| Node cur = open.top();
open.pop();
close.push_back(cur);
int x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
if (cur.map[i][j] == 0) {
x = i;
y = j;
break;
}
}
}
if (x > 0) {
Node next = cur;
next.map[x][y] = cur.map[x - 1][y];
next.map[x - 1][y] = 0;
bool flag = 0;
flag = checkSame(next);
if (!flag) {
next.h = H(next.map);
next.depth = cur.depth + 1;
next.id = ++count;
next.parent = cur.id;
open.push(next);
}
}
if (x < 2) {
Node next = cur;
next.map[x][y] = cur.map[x + 1][y];
next.map[x + 1][y] = 0;
bool flag = 0;
flag = checkSame(next);
if (!flag) {
next.h = H(next.map);
next.depth = cur.depth + 1;
next.id = ++count;
next.parent = cur.id;
open.push(next);
}
}
if (y > 0) {
Node next = cur;
next.map[x][y] = cur.map[x][y - 1];
next.map[x][y - 1] = 0;
bool flag = 0;
flag = checkSame(next);
if (!flag) {
next.h = H(next.map);
next.depth = cur.depth + 1;
next.id = ++count;
next.parent = cur.id;
open.push(next);
}
}
if (y < 2) {
Node next = cur;
next.map[x][y] = cur.map[x][y + 1];
next.map[x][y + 1] = 0;
bool flag = 0;
flag = checkSame(next);
if (!flag) {
next.h = H(next.map);
next.depth = cur.depth + 1;
next.id = ++count;
next.parent = cur.id;
open.push(next);
}
}
|
Check
前面提到,我们在取出一个未扩展状态后需要先检查其是否为目标状态,随后再进行扩展,现在就对检查进行讨论。当状态估值h为0时,代表状态为目标状态。因此,我们可以认定找到一个解,并输出步数和搜索空间(可指示算法运行时间)。而对于路径的回溯,我们需要从最终的状态开始,不断根据状态的parent属性,在close序列中查找id等于parent的状态,并将其加入path序列中。最后倒序输出path即为我们搜索到的求解路径。
CHECK1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| if (cur.h == 0) {
cout<<"找到解!"<<endl;
cout<<"步数:"<<cur.depth<<endl;
cout<<"搜索空间:"<<count<<endl;
cout<<"路径:"<<endl;
path.push_back(cur);
while (cur.parent != -1) {
for (int i = 0; i < close.size(); i++) {
if (close[i].id == cur.parent) {
path.push_back(close[i]);
cur = close[i];
break;
}
}
}
for (int i = path.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout<<"第 " <<path.size() - i - 1 <<" 步:\n";
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
for(int k=0;k<3;k++){
cout<<path[i].map[j][k]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<"曼哈顿距离:" <<path[i].h <<endl;
cout<<endl;
}
break;
}
|
三、程序测试
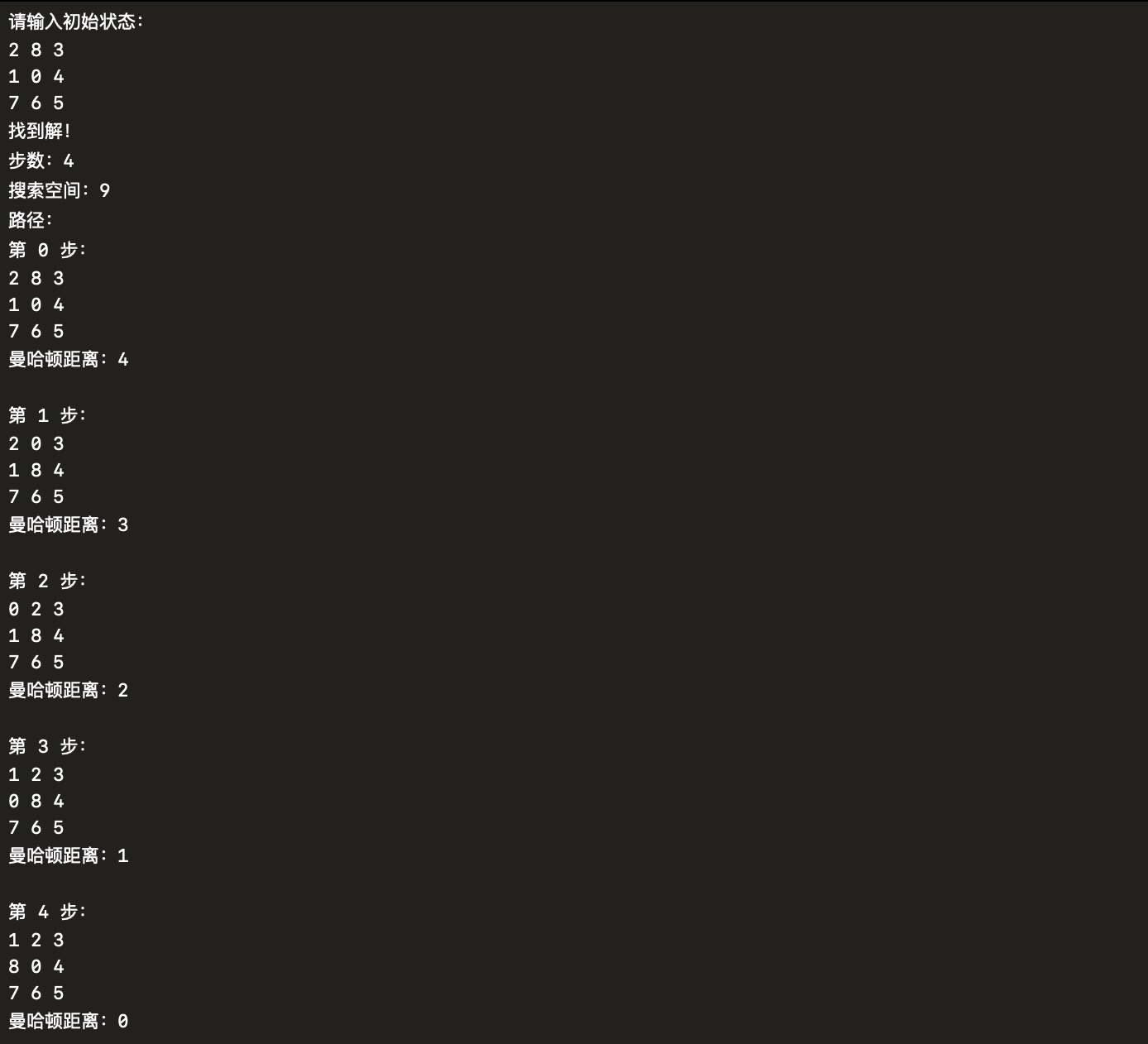
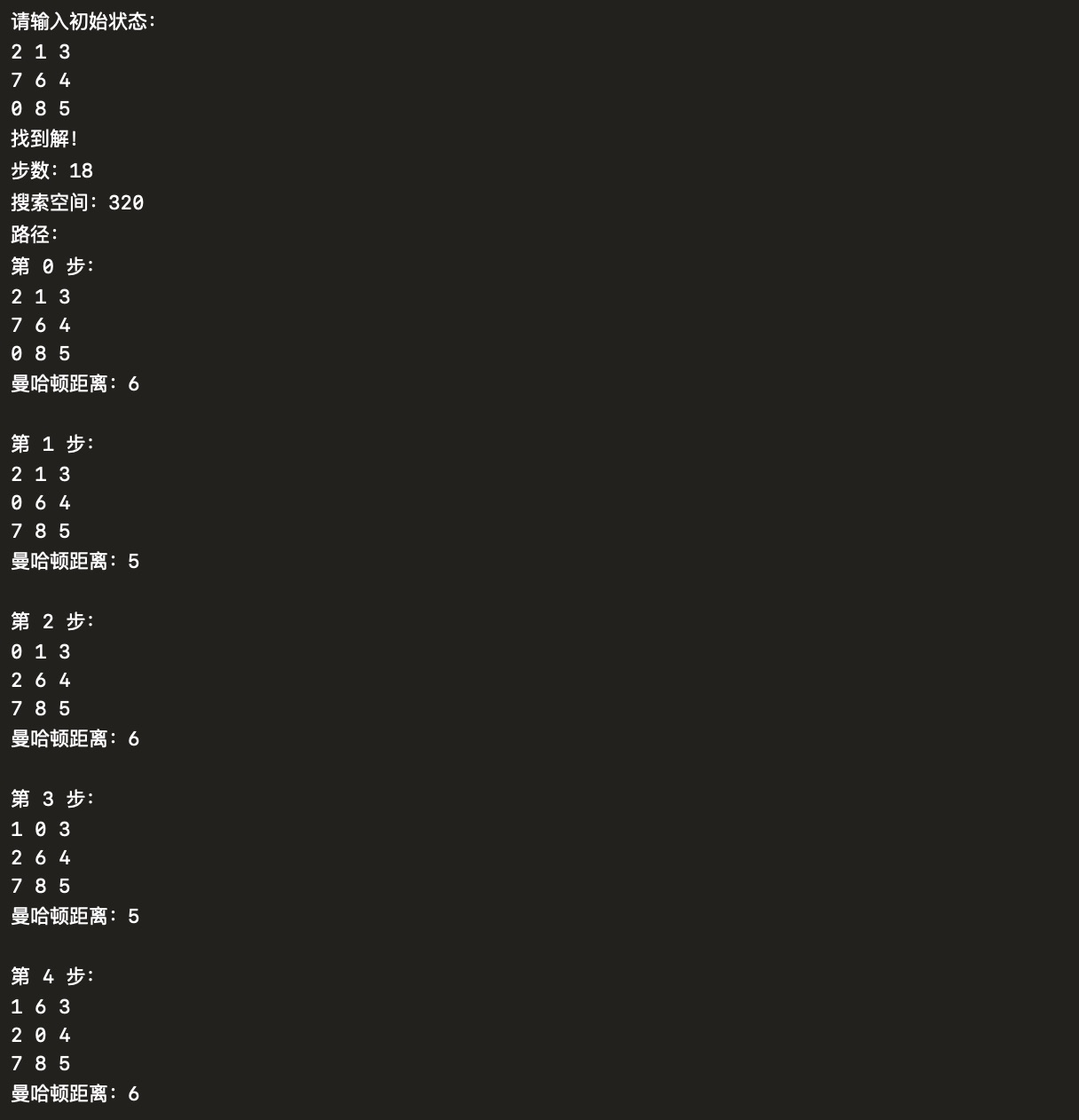
实验手册给出了两个测试样例,涵盖了步数较少和较多两种情况,我就直接拿来用了。
 test-1
test-1
 test-2
test-2
第二个样例的路径较长,就不全放了。
四、实验总结
这次实验的算法也比较简单,编码上搜索状态空间树的部分有点复杂,但难度也不大。而A算法最核心的就是启发函数的设计,实验直接给了4个函数备选,因此也没什么设计难度,编码实现即可。
五、源码
最后放一下全部代码。
CODE1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
| #include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int map[3][3];
int h, depth;
int id, parent;
};
struct cmp {
bool operator()(Node a, Node b) {
if(a.h > b.h)
return 1;
else if(a.h < b.h)
return 0;
else
return a.depth > b.depth;
}
};
priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, cmp> open;
vector<Node> close;
vector<Node> path;
int end_loc[8][2] = {{0, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, 2}, {1, 2}, {2, 2}, {2, 1}, {2, 0}, {1, 0}};
int H(int map[3][3]) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
int num = map[i][j];
if (num == 0) continue;
sum += abs(i - end_loc[num - 1][0]) + abs(j - end_loc[num - 1][1]);
}
}
return sum;
}
bool checkSame(Node t) {
for (int i = 0; i < close.size(); i++) {
bool same = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
if (close[i].map[j][k] != t.map[j][k]) {
same = 0;
break;
}
}
}
if (same)
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void print_info(Node cur) {
cout<<"当前状态:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
cout<<cur.map[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<"id: "<<cur.id<<endl;
cout<<"parent: "<<cur.parent<<endl;
cout<<"depth: "<<cur.depth<<endl;
cout<<"曼哈顿距离:"<<cur.h <<endl;
cout<<endl;
}
int main() {
Node start;
cout<<"请输入初始状态:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
cin>>start.map[i][j];
}
}
start.h = H(start.map);
start.depth = 0;
start.id = 0;
start.parent = -1;
open.push(start);
int count = 0;
while (!open.empty()) {
Node cur = open.top();
open.pop();
close.push_back(cur);
if (cur.h == 0) {
cout<<"找到解!"<<endl;
cout<<"步数:"<<cur.depth<<endl;
cout<<"搜索空间:"<<count<<endl;
cout<<"路径:"<<endl;
path.push_back(cur);
while (cur.parent != -1) {
for (int i = 0; i < close.size(); i++) {
if (close[i].id == cur.parent) {
path.push_back(close[i]);
cur = close[i];
break;
}
}
}
for (int i = path.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout<<"第 " <<path.size() - i - 1 <<" 步:\n";
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
for(int k=0;k<3;k++){
cout<<path[i].map[j][k]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<"曼哈顿距离:" <<path[i].h <<endl;
cout<<endl;
}
break;
}
int x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
if (cur.map[i][j] == 0) {
x = i;
y = j;
break;
}
}
}
if (x > 0) {
Node next = cur;
next.map[x][y] = cur.map[x - 1][y];
next.map[x - 1][y] = 0;
bool flag = 0;
flag = checkSame(next);
if (!flag) {
next.h = H(next.map);
next.depth = cur.depth + 1;
next.id = ++count;
next.parent = cur.id;
open.push(next);
}
}
if (x < 2) {
Node next = cur;
next.map[x][y] = cur.map[x + 1][y];
next.map[x + 1][y] = 0;
bool flag = 0;
flag = checkSame(next);
if (!flag) {
next.h = H(next.map);
next.depth = cur.depth + 1;
next.id = ++count;
next.parent = cur.id;
open.push(next);
}
}
if (y > 0) {
Node next = cur;
next.map[x][y] = cur.map[x][y - 1];
next.map[x][y - 1] = 0;
bool flag = 0;
flag = checkSame(next);
if (!flag) {
next.h = H(next.map);
next.depth = cur.depth + 1;
next.id = ++count;
next.parent = cur.id;
open.push(next);
}
}
if (y < 2) {
Node next = cur;
next.map[x][y] = cur.map[x][y + 1];
next.map[x][y + 1] = 0;
bool flag = 0;
flag = checkSame(next);
if (!flag) {
next.h = H(next.map);
next.depth = cur.depth + 1;
next.id = ++count;
next.parent = cur.id;
open.push(next);
}
}
}
}
|